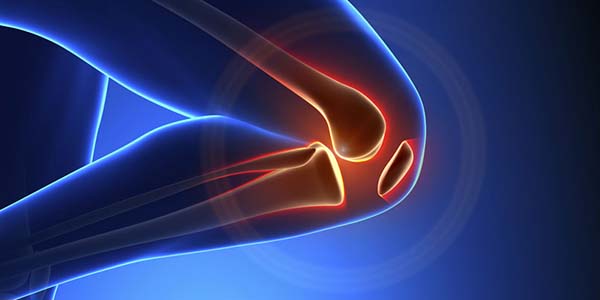
Only select tissues and organs are able to spontaneously regenerate after disease or trauma, and this regenerative capacity diminishes over time. Human regenerative medicine research explores therapeutic regenerative approaches to treat various conditions. Mesenchymal regenerative medicines (MSCs) are derived from adult regenerative medicines; they are multipotent and exert anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. They can differentiate into multiple cell types of the mesenchyme, for example, endothelial cells, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, fibroblasts, tenocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells, and sarcomere muscular cells. MSCs are easily obtained and can be cultivated and expanded in vitro; thus, they represent a promising and encouraging treatment approach in orthopedic surgery.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5494105/
Roberto Berebichez-Fridman, Ricardo Gómez-García, Julio Granados-Montiel, Enrique Berebichez-Fastlicht, Anell Olivos-Meza, Julio Granados, Cristina Velasquillo, and Clemente Ibarra